The method implies an underlying client-server architecture, in which te client is the process that calls the remote procedure, and the server is the process that executes the code and returns the result of the execution at the client.
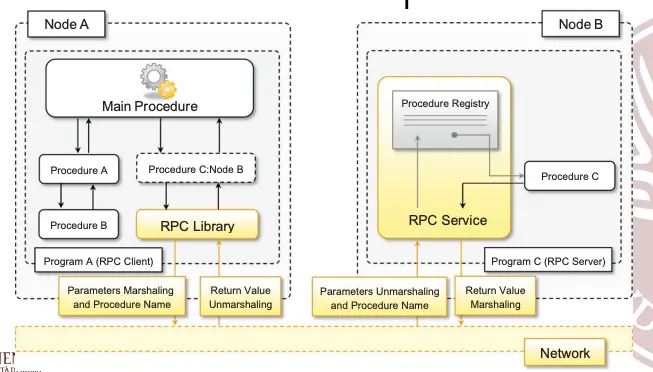
The client uses an RPC Library in order to make the call to a remote procedure.
The RPC library uses an RPC infrastructure, that is responsible for marshaling and unmarshaling the message (serializing and de-serializing) in formats like XML or JSON. These formats are preferred since they’re platform independent.
Some RPC APIs exists that are platform dependent, such as RPyC for Python or RPClib for C++.
The server decides which procedures to expose for remote invocation, which will be put on the Procedure Registry.
RPC is useful in distributed computation, where we want to invoke procedures that will be exectured on other nodes.
Distributed objects
Since RCP works with imperative programming, in order to use it with OOP we need Distributed objects.
Each process register a set of methods for a certain class that are accessible remotely. The client can invoke those methods, and the RCP infrastructure will convert the local method invocation into a remote procedure call request, collecting also the result of the execution.
The distributed objects model introduce a complexity regarding the state management. RPC is stateless, but this implementation is not, since the object is stored on the server, but the methods, that can modify the object properties, are called remotely, so each node has to have the up-to-date version of the object.
If a certain object has to be passes inside a certain method parameters, then the object can be passed by value, meaning a copy of the object is made on the server (this can cause some inconsistency problems); or by reference, meaning there is no duplication of the object, but the managment becomes more difficult.
An object on the server can be created on the server, meaning by the creator of the procedure (server-based); or on the client, meaning when a certain method is invoked (client-based).
Examples of distributed object frameworks are CORBA, .NET Remoting and RMI