A bitcoin is represented by a file that embeds the following informations:
- Numbers of bitcoins
- The owner, represented by the public key
- The hash of the file (in order to protect the integrity of the message)
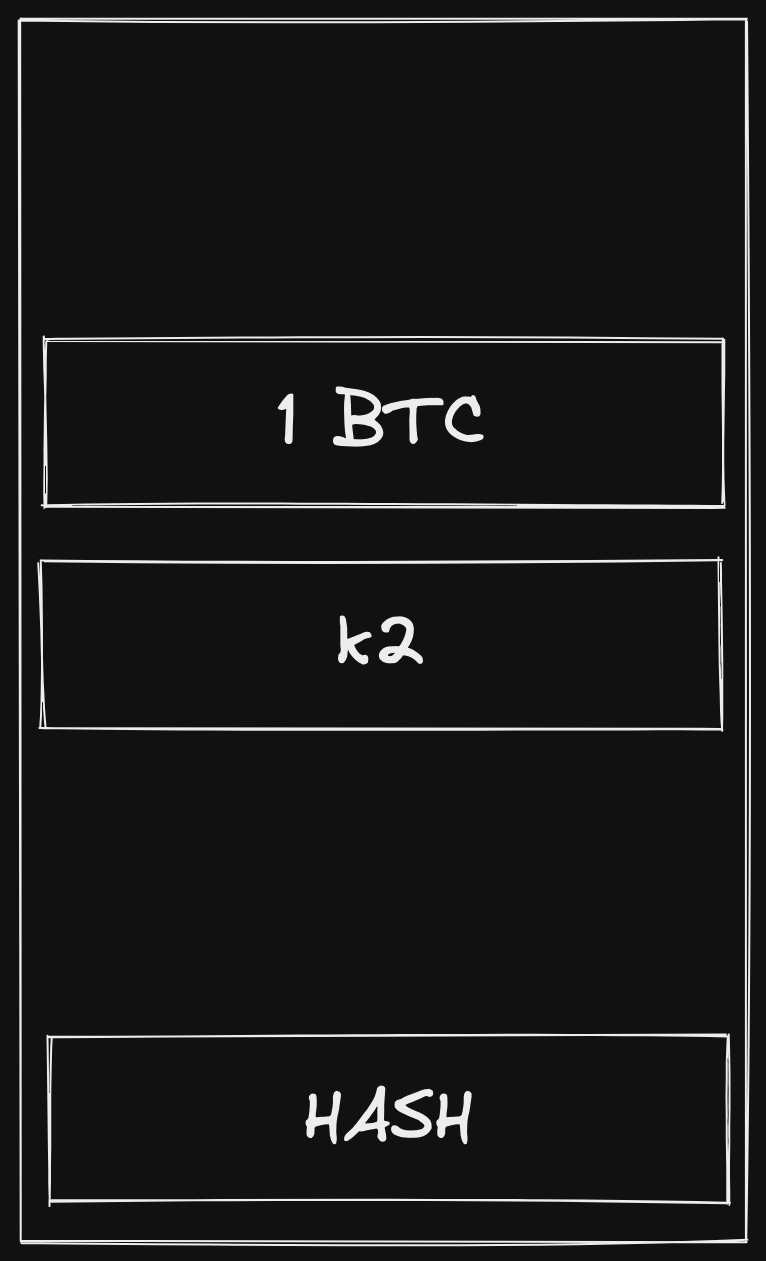
Bitcoin structure
If I want to make a transaction and give the bitcoin to someone else, let’s assume the other person’s public key is , I have to prepare a new file that embeds the following informations:
- The same hash of the file I own;
- The new owner, represented by the public key
- The signature, meaning the hash of the entire file encrypted with my private key
To make a transacton you need the private key, to check it just the public key is needed. If the private key is lost, then those bitcoin are lost and cannot be given to anyone anymore. If someone steals your private key, also those bitcoin are lost since they can make a transaction.
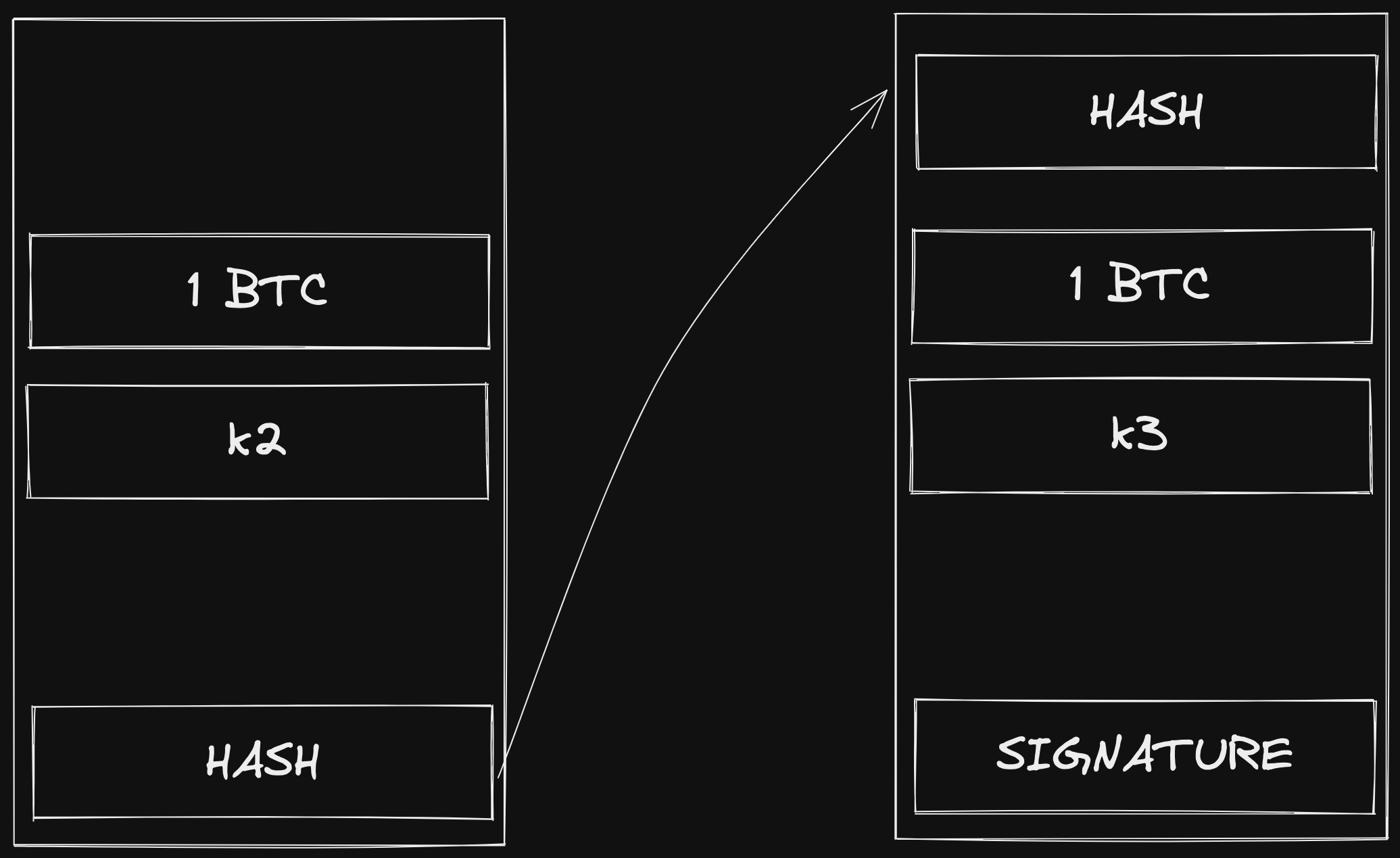
Transaction
There is a fundamental problem in this procedure, that’s called double spending. Nothing prevents me from giving the same bitcoin to two different people. This problem is solved with the construction of a blockchain.
