Euclidean distance
The Euclidean distance measures the length of a straight line connecting two points.
Pythagoras’ theorems says:
In matrix notation we can write the same thing:
The Euclidean distance can also be called the -Norm.
The norm (or length) of a vector is simply its distance from the origin:
distance
The distance is a generalization with differnt coefficient of the Euclidean distance.
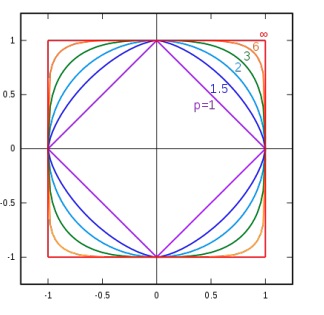
distance in with different values for .
Note
Note that the number of dimensions for points in and the coefficient are two different things.