Todo
This has to be reviewed
Let be the output of the -th layer in the network defined as:
If you compute the average and the standard deviation of the data points at the layer and those of the data points at layer , these would be different. This is expected since it means that the network is doing something with the data, but researchers said that is not good for the network.
The phenomenon is called internal covariate shift, meaning that the distribution of the data shifts across the layers of the network.
Researchers showed that by re-normalizing before passing it to the next layer, the results were better.
This procedure takes the name of batch normalization.
Formally:
where is the training set that has reached level of the network.
Note that since we are applying the normalization in the forward pass, we must be able to backpropagate through it, and so the operation has to be differentiable, meaning we have to be able to compute
The normalization happens in this way:
Where the expected value (mean) and variance are computed over the training set. After the transformation, the data points will have mean and variance .
Trainable weights
Generally, in a neural network is should be possible that one layer does nothing to the data, meaning it will represent the identity. With batch norm this isn’t possible, since the data is normalized, and so modified.
In order to allows this, we introduce two trainable weights and in the transformation:
In this way the network can learn those weights, and if is equal to the variance and is equal to the mean, then the normalization won’t happen, hence the layer represent the identity ().
Mini-batches
Since now we always normalize the data points with respect to the entire training set. Since most of the time we use SGD with mini-batches, we should be capable to use batch normalization with mini-batches.
We can do that by simply taking each time the mean and variance with respect to the current mini-batch. This also increases the robustness of the network, since normalizing means expressing each datapoint in terms of the other data points in the mini batch. The interaction is each time local to the mini-batch, but since the mini-batch changes each time, each time the data points interact with different other datapoints.
At test time mini-batches don’t exist anymore, so it’s not clear with respect to who we have to normalize. The solution is to remember and aggregate the means and variances computed during the training step, and use those also in the testing set.
Batch Norm Variants
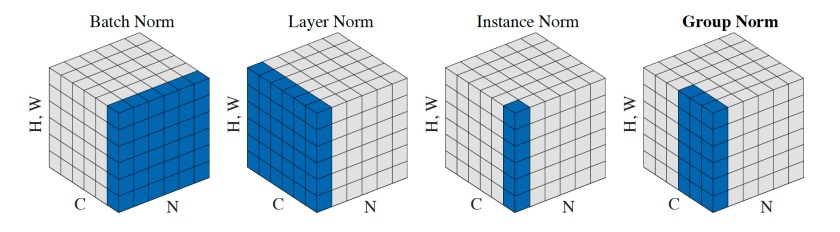
Batch normalization performs the normalization across the datapoints. There are variants of the batch norm in which you can normalize the data with respect to other things.
- Layer norm normalizes across the channels of the data.
- Instance Norm normalizes across the dimensions of the data;
- Group Norm is like layer norm but with a subset of the channels.
Normalizing with respect to something means to compute the mean and variance with respect to that something.
Everytime you change what is being normalized, that is a variant of the Batch Normalization.