All classic Deep Learning methods have one thing in common: they use some sort of embedding, which is then compared to other embeddings with some type of distance, like cosine or L2, in an euclidean space.
The problem with the euclidean space is that they are not suitable for representing hierarchical data, since two points that have a big distance in the euclidean space might still be very similar in the hierarchical sense.
We can observe what causes this by drawing a tree on a 2D plane, and a circle around the tree.
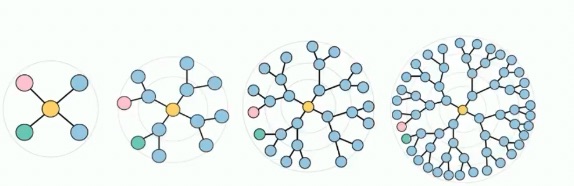
For example, in the provided drawing, the pink and green nodes have a small Euclidean distance, even though they come from two different subtrees.
The problem is caused by the fact that the circumference has a linear relationship with respect to the ratio , while the number of children grows in an exponential manner.
In the hyperbolic space this doesn’t happen, since the ratio grows exponentially with respect to the circumference. This is due to the fact that hyperbolic space, and specifically the Poincaré Ball Model, maps all the infinite points of the euclidean space into a sphere of radius . This means that the Poincaré distance between two points and also depends on the hyperbolic radii of and . Which means that distances near the circumference will be higher than near the center.
Where is a function that grows exponentially.
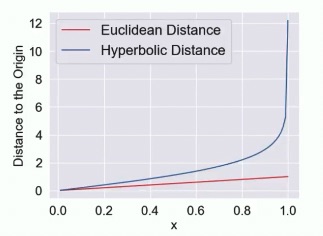
By embedding points into the hyperbolic space we are able to better represent hierarchies with minimal distortion.
The first successes with this kind of approach were in NLP, since text embeddings have a very hierarchical nature.
In computer vision, image collections are commonly hierarchical, meaning you can have a photo of a monument, and then some pictures of a part of that monument more in detail, etc.
We can use the hyperbolic radius to encode uncertainty in the learning process. So if the model is certain about something and it’s wrong about it, it will get a penalty exponentially higher w.r.t to the certainty. On the other hand, if it’s uncertain and wrong, it will get penalized less.
The hyperbolic radius of a point in the hyperbolic space is a good proxy for uncertainty since if two points are near the center, their distance will be lower, while near the circumference will be higher.
Hyperbolic is not a standard yet for many reasons:
- Our school teaches geometry in the euclidean space
- All the powerful deep learning frameworks work in the euclidean space
- The computers work best with euclidean data.
It’s possible to add an Exponential mapping, which maps the embeddings to the Poincaré ball, in order to transform an euclidean network into an hyperbolic network.
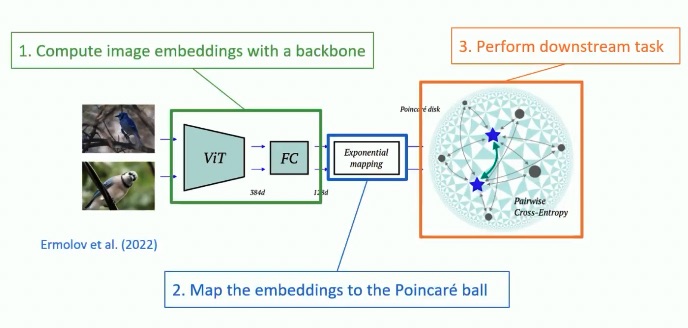
Also the loss will be based on hyperbolic distance, in order to be able to encode hierarchies or the uncertainty.